ADULT MAPLESON CIRCUITS
Product Details:
ADULT MAPLESON CIRCUITS Price And Quantity
- 1550 INR/Piece
- 10 Piece
Product Description
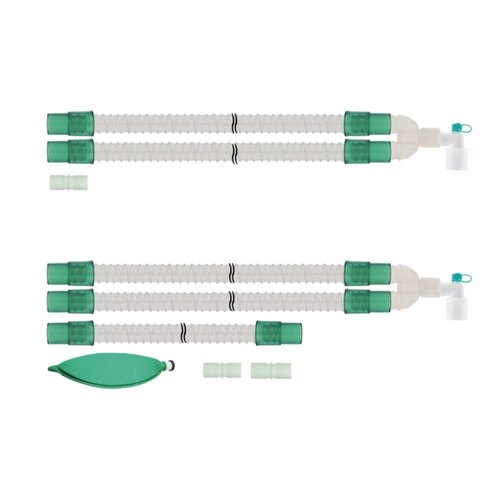
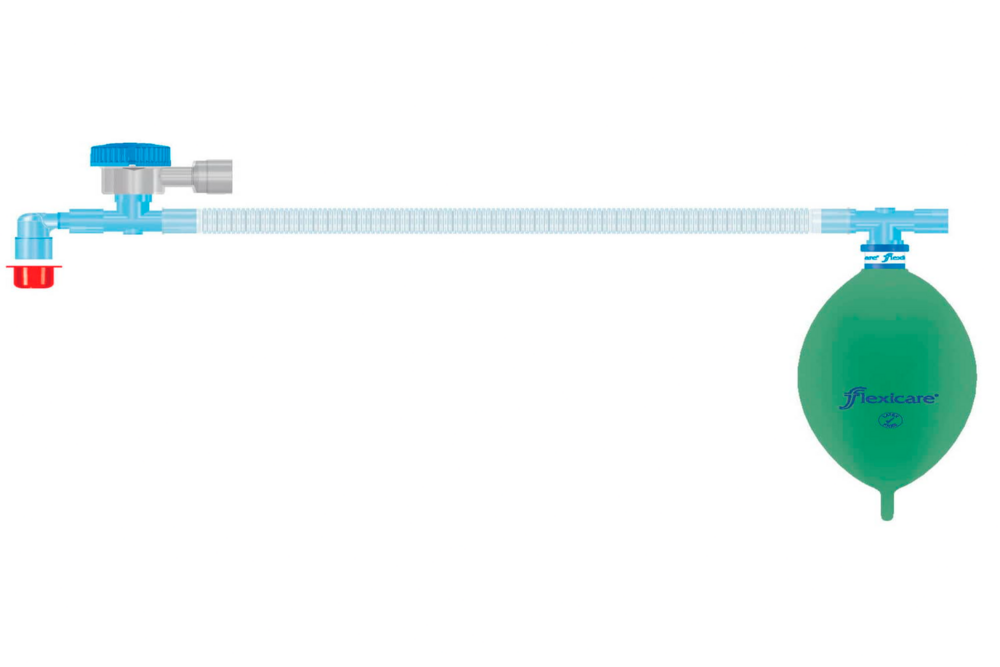
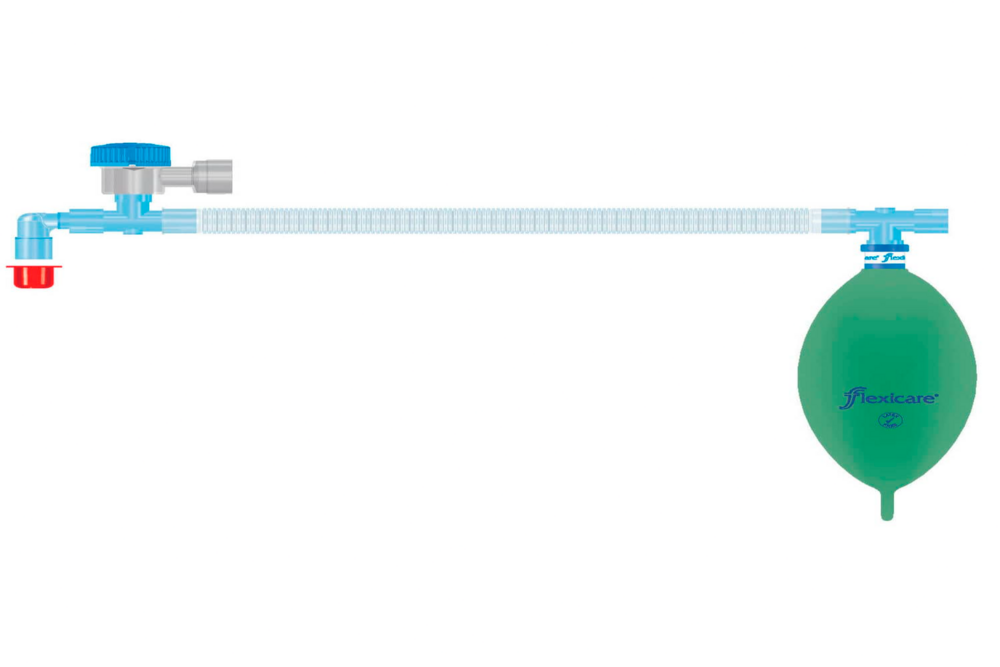
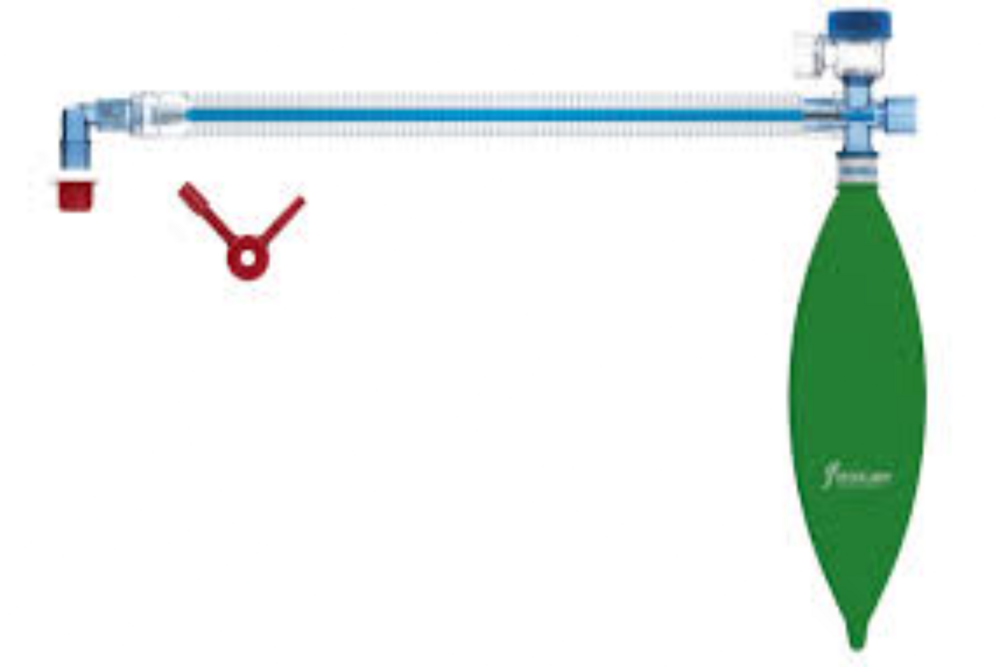
Mapleson CircuitAdult Mapleson circuits are semi-closed breathing systems used in anesthesia that vary in their efficiency and application depending on the specific type. Here are the key points about adult Mapleson circuits:
-
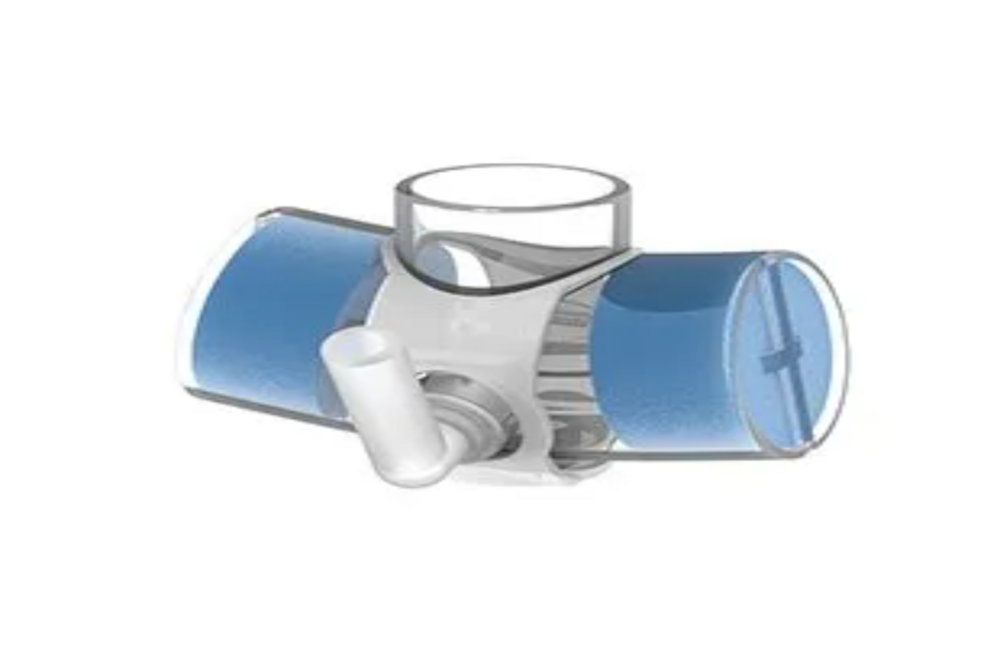
Mapleson A: This system is the most efficient for spontaneous ventilation in adults. It consists of a reservoir bag at the machine end and an adjustable pressure-limiting (APL) valve at the patient end, separated by 110-180cm of tubing. Fresh gas flow equivalent to the minute volume is sufficient to prevent rebreathing.
-
Mapleson B & C: These systems are similar, with the B system having longer tubing than the C system. Both are inefficient for both spontaneous and controlled ventilation, requiring high gas flows to prevent rebreathing. The C system is commonly used during patient transfer and in resuscitation due to its compact design.
-
Mapleson D: This system is efficient for controlled ventilation but inefficient for spontaneous ventilation. It features the fresh gas flow introduced at the patient end, with the APL valve and reservoir bag at the machine end, separated by 180cm of tubing.
-
Mapleson E: Also known as Ayre™s T-piece, this system is used for pediatric patients but can also be used for adults. It is efficient for both spontaneous and controlled ventilation.
-
Mapleson F: This is a modification of the Mapleson E system, incorporating a reservoir bag for both spontaneous and controlled ventilation, and is suitable for neonates and pediatric patients.
Each Mapleson circuit has specific requirements for fresh gas flow rates to prevent rebreathing, with the Mapleson A requiring a flow equivalent to the minute volume, while others may need higher flows.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free
